Spatial QUEFTS¶
Sebastian Palmas and Robert Hijmans
Introduction¶
Here we show how to spatially model QUEFTS. We will run an example using data from Tanzania.
Chapter requirements¶
We use the R packages Rquefts, terra and reagro. See
these instructions about installing these
packages.
Soil data¶
We use soil raster data from SoilGrids. We changed the pH values from the original data source by dividing them by 10 to get the correct numbers.
library(reagro)
SOC <- reagro_data("TZA_ORC")
Kex <- reagro_data("TZA_EXK")
pH <- reagro_data("TZA_PH")
Need to fix this, there is P data in soilgrids:
“There is no P olsen raster in soilgrids, in the code below we create a constant P Olsen layer by using the soilC layer as a template and assigning all cells a value of 15.”
From these chemical soil properties, we can use QUEFTS to compute the soil nutrient supply.
library(Rquefts)
supply <- rast(pH, nlyr=3)
values(supply) <- nutSupply(pH, SOC, Kex, Polsen=15)
supply
## class : SpatRaster
## dimensions : 1191, 1210, 3 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
## resolution : 1000, 1000 (x, y)
## extent : 1037375, 2247375, -1841875, -650875 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
## coord. ref. : +proj=laea +lat_0=5 +lon_0=20 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
## data source : memory
## names : lyr.1, lyr.2, lyr.3
## min values : 8.283516, -30.404197, -1.779519
## max values : 742.1297, 52.7725, 89.2500
We have some negative values (let’s remove them. Let’s see what happens when we use real P values)
supply <- clamp(supply, 1, Inf)
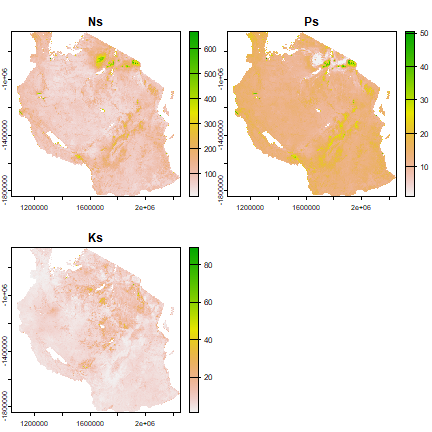
names(supply) <- c("Ns", "Ps", "Ks")
supply
## class : SpatRaster
## dimensions : 1191, 1210, 3 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
## resolution : 1000, 1000 (x, y)
## extent : 1037375, 2247375, -1841875, -650875 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
## coord. ref. : +proj=laea +lat_0=5 +lon_0=20 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
## data source : memory
## names : Ns, Ps, Ks
## min values : 8.283516, 1.000000, 1.000000
## max values : 742.1297, 52.7725, 89.2500
plot(supply)
Water limited yield¶
For attainable yield, we use a raster of water-limited yield estimated by the GYGA project.
Ya <- reagro_data("TZA_YW")
Running QUEFTS¶
library(Rquefts)
maize <- quefts_crop("Maize")
fertilizer <- list(N=64, P=20, K=0)
q <- quefts(crop=maize, fert=fertilizer)
In this example, 64 kg/ha of N and 20 kg/ha of P comes from using 100 kg/ha of Urea and 100 kg/ha of DAP.
yield <- rast(Ya)
values(yield) <- run(q, supply, Ya)
plot(yield)